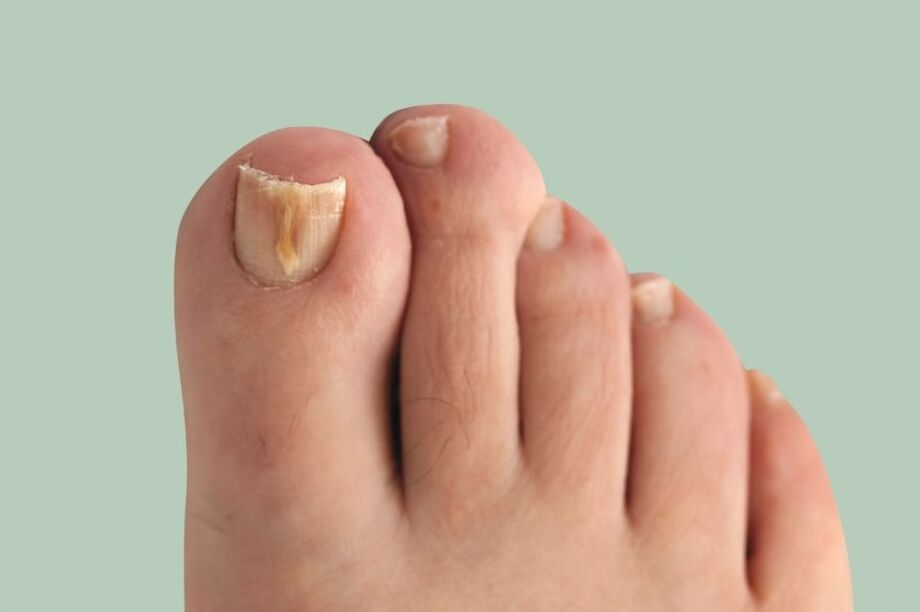
Onychomycosis(nail fungus) is a fungal infection of the nail plate and the structures around it: the nail folds, the matrix (the growing part of the nail) and the nail bed. Deformation and thickening of the nails manifests itself as a change in color - the nails become white or yellow.
This disease is quite common. According to some reports, the prevalence of onychomycosis in Europeans reaches 10-12%, which exceeds the known indicators of the previous decade. It occurs 1. 5 times more often in men, but they consult a doctor 2 times less often than women. Older people get sick more often, and children very rarely.
The main problem in the treatment of the disease is that patients consult a dermatologist for a long time after the first symptoms appear. For this reason, the pathological fungus covers a large area and the treatment is delayed.
Pathogenic fungi can only be transmitted by a sick person. Often, fungal infection occurs within the family, because the source is not identified in time and adequate preventive measures are not taken.
Causes of the disease:most often comes into direct contact with the patient or with the things he uses (shoes, clothes, bath mats, washcloths, manicure accessories). Infections often occur when visiting gyms, baths, saunas and swimming pools.
The development of the disease is facilitated by microdamages - cracks in the interdigital folds caused by abrasion, excessive sweating, dry skin, poor drying after water procedures and flat feet.
Nail mycoses can also occur with accompanying diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism), vascular diseases of the extremities (venous insufficiency, lymphostasis), immune disorders, as well as the use of antibiotics and corticosteroids. cytostatic drugs. As a result of the above-mentioned diseases, blood microcirculation in the nail area is disturbed and natural immunity decreases, which contributes to the development of secondary infection.
Onychomycosis is caused by the following types of fungi:
- dermatophyte;
- Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida;
- mold fungi.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the penetration of the fungal infection and the clinical picture occur differently, so the approaches to therapy also differ.
Toenails are 10 times more affected by fungus than nails. In most cases, the fungus is caused by dermatophytes (for example, Trichophyton rubrum). The remaining cases are mostly caused by non-dermatophytic molds (Aspergillus, Scopulariopsis, Fusarium).
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Along with nail fungus, athlete's foot can also develop. Mycosis of the feet (dermatophytosis, Tinea pedis) is a disease of the skin of the feet caused by pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. Skin changes on the legs are characterized by peeling accompanied by itching. In case of severe injuries, against the background of reddening and swelling of the skin, erosion and deep cracks are formed in the legs and in the spaces between the toes, which are accompanied by pain and make it difficult to walk.
The emergence of modern antifungal drugs has improved the epidemiological situation, but mycosis of the feet still remains one of the most important problems of dermatovenerology. The use of some drugs is restricted in elderly people and patients with chronic diseases.
Ways of infection
The risk of fungal infection is especially high in public places with high humidity. These are saunas, swimming pools, gyms, baths, etc. The most common ways of infection:
- direct contact with an infected person. Here, the fungus moves from the habitat to healthy areas, thereby causing infection;
- household road. In this case, the infection occurs when using the patient's personal items: shoes, personal hygiene items, etc.
Risk factors
The frequency of onychomycosis increases up to 60 years of age. At this time, the probability of developing such an infection is 60%, which is explained by the slowing down of metabolism, especially in the distal (distant) parts of the body, such as the fingers and toes.
Other risk factors for developing nail fungus include:
- diabetes;
- varicose veins;
- damage to nails and adjacent tissues;
- HIV and other immunodeficiency conditions;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- weakened immune system;
- vascular and skin diseases, dermatitis, diaper rash;
- violation of blood supply to the extremities;
- insufficient hygiene.
Symptoms of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
The longer the disease lasts, the more pronounced its symptoms are. The main symptoms of onychomycosis include:
- dyschromia - nail color changes to yellow, black, green, gray or brown (the type of color depends on the type of fungus);
- onycholysis - separation of the nail plate from the bed;
- change in the thickness of the nail plate;
- hapalonychia - a decrease in the thickness of the plate and its softening;
- koilonychia - the nail appears concave in the shape of a teaspoon;
- pachyonychia - thickening of the nail plate, nail hypertrophy;
- onychogryphosis - thickening of the nail plate, discoloration, curved in the form of a beak;
- change in the thickness of the nail bed (hyperkeratosis - thickening of the nail bed);
- changes in the surface of the nail plate: pits, grooves, ridges;
- changes in nail folds and surrounding skin (paronychia - inflammation of the proximal layer of nails).
It should be noted that none of the symptoms are pathognomonic, that is, unique to a particular pathogen, so it cannot be identified by symptoms - additional examinations are needed.
Pathogenesis of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
The pathogenesis of the disease depends on how the fungus enters the skin and nails.
Distal subungual type:if the fungus penetrates the nail folds or the skin in the distal region, the infection spreads from the free edge of the nail bed and further into the matrix. At first, the nail plate may not change, but later, due to hyperkeratosis, it gradually moves away from the nail bed and becomes yellowish. The nail plate may gradually thicken.
Type of surface white:If whitish spots appear on the nail surface, the fungus will cover the entire nail plate over time. The nail thickens, collapses and acquires a gray-brown color. In this case, the matrix and epithelium of the nail bed are not affected. There is no inflammation of the surrounding skin.
Proximal subungual type:the fungus can spread from the skin and periungual folds to the nail plate and further into the matrix, reaching the distal parts of the nail plate. Spots appear in the nail pit and nail bed area, and the nail plate breaks off. There is no significant inflammation of the nail bed or matrix.
General dystrophic type:The entire nail is affected. The proximal parts of the nail fold disappear or thicken so that the nail plate can no longer form or grow.
AvailableBiophysical concept of the pathogenesis of onychomycosis, states that during disease there is a conflict between two forces: the fungal colony growing toward the matrix and the natural growth of the nail from the matrix to the distal edge. Therefore, the speed of nail growth during onychomycosis is decisive - the faster the nail grows, the faster the treatment will take place. Perhaps this explains the low prevalence of the disease in children, because their nails grow faster than adults and the elderly.
Classification and development stages of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Onychomycosis has the following classification:
- distal subungual;
- surface white;
- proximal subungual;
- completely dystrophic.
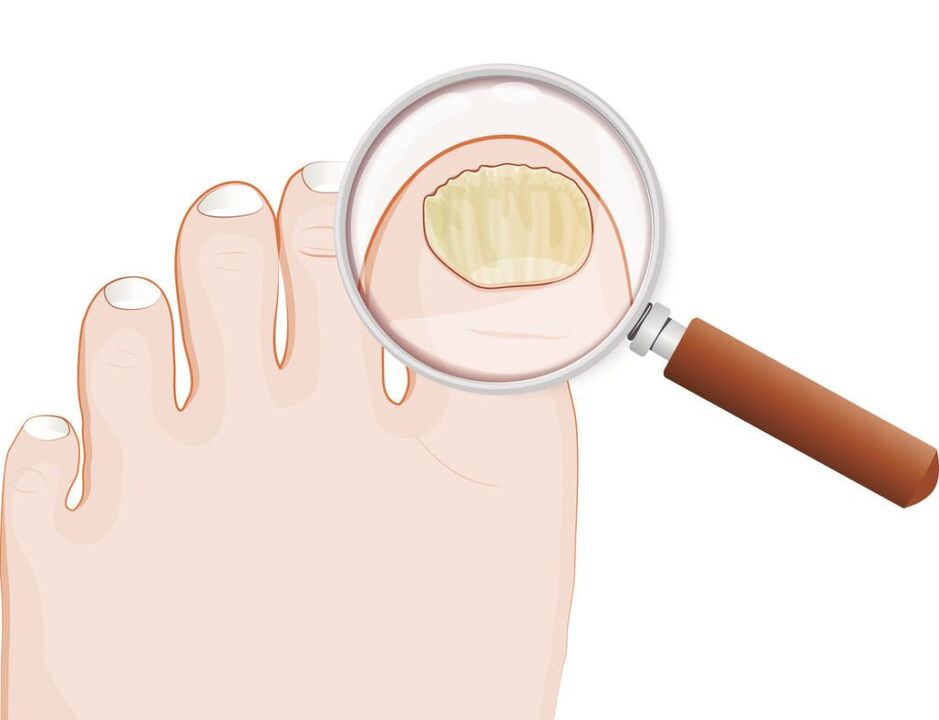
According to Ariyevich's classification (1970):
- normotrophic: there are yellowish and whitish stripes in the thickness of the nail, but the shape of the nail plate does not change, there is no subungual hyperkeratosis;
- hypertrophic:the nail plate turns yellow, thickens due to subungual hyperkeratosis, becomes brittle, the edges are curved;
- dystrophic:thinning of the nail plate and separation from the nail bed occurs with the formation of gaps.
Complications of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Long-term onychomycosis increases the risk of developmentdiabetic foot(formation of trophic ulcers on the legs) andgangreneif the patient has diabetes mellitus or vascular diseases of the lower extremities.
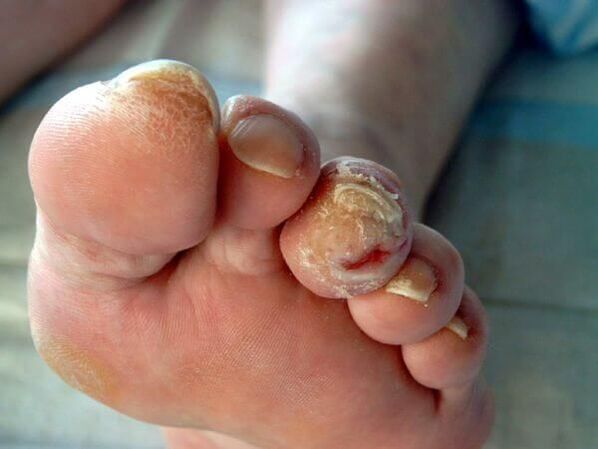
In immunosuppressive conditions (primary and secondary immunodeficiencies), fungi can spread to the skin, internal organs and cause allergies in the body. This can manifest itself as skin rashes and even the development of bronchial asthma.
In an uncomplicated course, the disease causes traditional symptoms for a fungus, causing only severe discomfort in a person. However, without treatment, onychomycosis can cause complications. Often, they manifest themselves in the addition of a bacterial infection.
Sometimes onychomycosis is very acute with the appearance of blisters, ulcers and weeping areas on the skin near the nail. In severe cases, the disease takes a generalized form. This means that the nail fungus spreads to internal organs and systems, and then the patient will require urgent hospitalization.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Before examining the methods of diagnosis of onychomycosis, it is necessary to explain how to properly collect the material for the study (the patient does it independently or prepares the nails before the diagnosis). Before collecting material for research, it is necessary to treat the nail plate with 70% alcohol to avoid contamination with other bacteria.
The method of material collection varies depending on the form of onychomycosis:
- surface form- scraping from the nail plate;
- distal form- both a scrap from the nail bed and a piece of the nail plate are needed;
- proximal subungual form- the material is collected with a drill, or a nail biopsy is performed, or a scraping is performed from the nail bed.
It is the fastest way to determine the pathological fungus on the nailmicroscopy. Technique: the studied material is treated with an alkaline solution to dissolve the keratin. Ink is added to the alkali to make the mushroom stalks look better. Then, the resulting preparation is studied under a microscope.
This research method is the fastest and most objective. Sensitivity is up to 80%. The disadvantages of the method are that it is not possible to determine the type of pathogen when using it.
Bacteriological culture: is an additional method for the diagnosis of onychomycosis. The material is sown in a special medium and the result is interpreted under a microscope after 2-3 weeks. This method allows to determine the type of pathogen - it helps to determine treatment tactics and select drugs based on sensitivity. But the disadvantage of the research is that it takes a lot of time and its sensitivity is only 30-50%.
Biopsy: Using a scalpel and applying anesthesia, the nail and nail bed are cut. The material is immersed in a formaldehyde solution and sent to the laboratory for histological examination. The advantages of this method are high sensitivity and allow to determine the presence of pathological fungi in the material.
Disadvantages: it is impossible to identify the pathogen, as well as to determine the viability of microorganisms, the method is expensive and labor-intensive.
Gene diagnostics: molecular biological research method (PCR). This is one of the new and highly sensitive methods for the diagnosis of onychomycosis - it helps to detect the DNA of the causative agent of the disease. In our country, it is recommended to use this type of diagnostics in medical institutions with PCR laboratories, but currently it is planned to use test systems that identify dermatophytes and molds only in laboratories. The method allows to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity ranges from 80-90%. Disadvantages: high cost, unavailability, lack of technology standards and complexity of implementation.
Increasingly, doctors are putting it into practicedermatoscopy. Using this method, you can evaluate changes in the color and structure of the nail, as well as the condition of the surrounding structures. Dermatoscopic examination allows more accurate assessment of the depth of damage to the nail plate and more accurate calculation of the severity index of onychomycosis (KIOTOS).
First, the patient is sent for microscopy, which allows to determine the presence of the pathogen. In order to choose the right treatment for nail fungus in the future, it is necessary to determine its type. At Tibb OJSC (academician Roitberg's clinic) located in the center of Moscow, the most up-to-date and widespread methods are used to diagnose onychomycosis:
- cultural examination of a biological sample of the affected tissue. For this purpose, it is placed in an artificial food medium where the pathogen is grown to determine its type;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method to detect pathogenic DNA in an affected tissue sample.
When to consult a doctor
Many people who experience onychomycosis know that the disease develops slowly and is incredibly difficult to treat. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear. Onychomycosis of the nails is treated by a dermatologist in our clinic in the center of Moscow. The specialist will provide competent assistance and guide you until complete recovery.
He is about to go to the doctor
Before visiting the dermatologist, it is important not to treat the affected areas of the nails with anything, i. e. Do not use drugs including iodine and bright green. Antifungal creams and ointments should also be avoided. During the appointment, you must pass all the previously obtained tests, including those for other diseases. Affected nails should not be cut 3-4 days before the consultation.
Treatment of onychomycosis (nail fungus).
There are several treatments for onychomycosis:
- Local therapy.
- Systemic therapy.
- Combination therapy.
- Corrective therapy.
Local therapyinvolves the application of drugs to the nail plate and nail folds. Indications for local therapy:
- Limited form of damage to the nail plate (according to KIOTOS).
- There are contraindications for prescribing systemic drugs: sensitivity, liver disease, renal dysfunction, pregnancy, lactation.
The advantages of this therapy are that a high concentration of the therapeutic agent is formed on the surface of the nail, which does not penetrate into the bloodstream. The use of antifungal drugs has no side effects - nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain. The disadvantage of the method is that the medicinal substance does not always reach the place of residence of the pathogen, especially if the fungus is located in the nail bed or matrix. This, in turn, can lead to treatment failure. This type of treatment requires a lot of labor, because before applying the medicine, you have to remove the affected part of the nail.
Methods of removing affected nails:
- Mechanical removal using files, nippers or a drill.
- Use of keratolytic patches. Before applying the keratolytic plaster, the skin around the nail is closed with a plaster, a plaster mass (urea with salicylic acid) is applied on top and closed with an adhesive plaster. The plaster mass is changed every 2-3 days. After each removal, the affected part of the nail is removed mechanically.
- Surgical. This operation is very painful and traumatic, because when the nail plate is removed, the growth zone can be damaged, which causes the deformed nails to grow back.
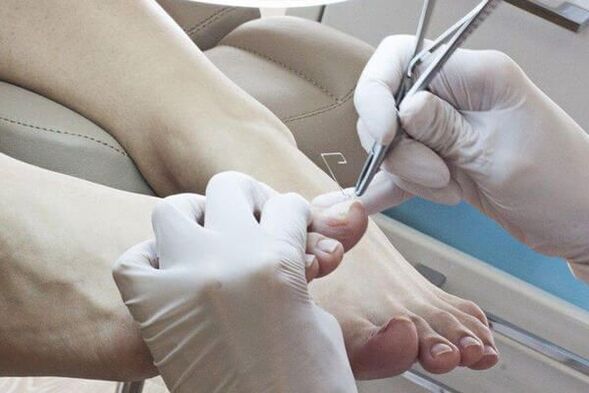
After removing the affected nail plate, local antifungal agents are used.AntimycoticsIt is distinguished by the place of application:
- applied to the nail: varnishes;
- applied to rolls: creams, ointments, solutions.
The most studied drug for local use1% Naftifin solution, has an evidence base for treatment efficacy based on a Cochrane meta-analysis. This product is water-based, which facilitates better penetration of the antifungal agent into the affected area. Lacquers with active ingredients ciclopirox and amorolfin have a dehydrated base, which reduces the penetration of the drug into deep layers. Therefore, dermatologists consider the use of varnishes unsatisfactory and increasingly prefer water-based products.
To get results from local therapy, it is necessary to follow the treatment regimen, it is important for the patient to be responsible, consistent and patient. The duration of therapy can be up to 12 months.
Systemic therapyeven if the nail bed and matrix are affected, it allows the antifungal drug to penetrate into the bloodstream at the site of the lesion. A high concentration of the drug remains in the affected area for a long time after use. The disadvantages of this type of treatment are associated with the risk of side effects and toxic effects.
Indications for systemic therapy:
- Common forms of damage to the nail plate.
- Lack of effect of local therapy (i. e. healthy nails did not grow after six months of treatment of onychomycosis of the hands and 9-12 months of treatment of onychomycosis of the feet).
In 1999, A. Yu. KIOTOS (Clinical index for assessment of severity of onychomycosis by Sergeev) proposed by Sergeev is used. It is used as a therapeutic standard in different countries of the world.
MedicinesFor the treatment of onychomycosis, it can be classified as follows:
- antimycotics - have an antifungal effect;
- antiseptics - have both antifungal and antibacterial effects. They are rarely used, only in the absence of other antifungal agents;
- multicomponent - in addition to the antifungal agent, they also contain other drugs such as anti-inflammatory drugs.
Recipe Modes:
- standard - to take daily medication during the prescribed treatment period;
- shortened - the duration of treatment is shortened, it can be carried out in regular doses or increased;
- intermediate - treatment is prescribed in several short courses, the breaks between courses are equal to the duration of the courses;
- pulse therapy - treatment is prescribed in several short courses, the intervals between the courses are longer than the duration of the courses.
Antifungal drugs are divided according to the active substance:
- triazoles;
- allylamines;
- others (third generation drugs).
It is currently used for systemic therapyonly third generation drugs.
With combination therapylocal and systemic treatment is carried out at the same time. Combined therapy is used when it is necessary to increase the effectiveness of systemic therapy and reduce the duration of treatment.
Corrective therapy(treatment of concomitant diseases): to choose the treatment regimen, it is necessary to evaluate the general somatic condition of the body. Diseases such as circulatory disorders in the extremities may reduce penetration of the antifungal agent into the lesion. Therefore, drugs that improve tissue trophism are prescribed.
Due to the toxic effect of systemic antifungal drugs, it is necessary to exclude liver disease and prescribe hepatoprotectors if necessary.
Home treatment
You should consult your doctor before using home remedies. With his permission, you can use the following recipes:
- iodine. Before use, the feet should be steamed, washed with laundry soap, and then the affected areas of the nail plates should be removed. Then treat the nails and skin between the fingers with iodine, soak in a bath with soda solution for 20-30 minutes and dry well;
- vinegar. Take 1 tablespoon for 3 liters of water. add apple cider vinegar and a little potassium permanganate. Keep your feet in the bath for 20-30 minutes, then dry them well;
- hydrogen peroxide. After thoroughly steaming your feet, remove the affected areas of the nail plates. Put cotton pads soaked in hydrogen peroxide on them, wrap with a bandage and leave for half an hour.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of nail fungus
One of the most important and dangerous myths is that nail fungus is not considered a serious disease. In fact, as it progresses, onychomycosis can lead to serious consequences, including deformation and complete rejection of the nail from the nail bed.
In addition, the infected person poses a daily threat to his loved ones, because they are also at risk of getting sick by being with him. Therefore, it is important to know how to treat nail fungus in time.
Forecast. Prevention
The sooner a patient consults a doctor with symptoms of a fungal nail infection, the sooner the disease can be treated and the nail plate can be restored. With long-term processes involving the entire nail, the treatment of onychomycosis can be long, but if all recommendations are followed, there is often recovery. If there are contraindications to systemic therapy, long-term maintenance treatment with local drugs is necessary.
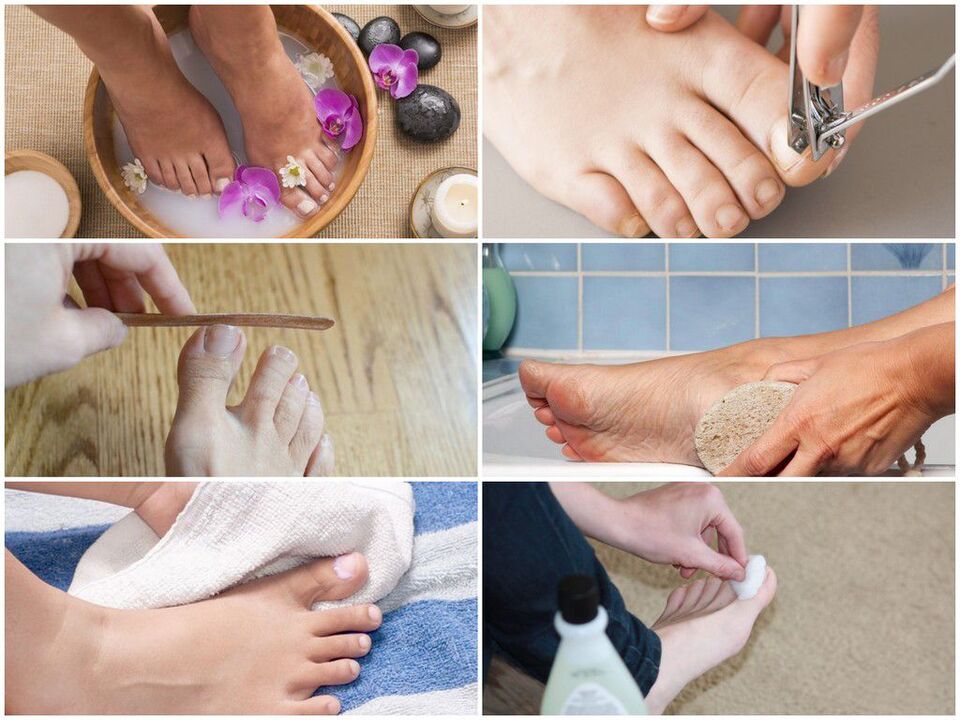
For preventionIt is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene and reduce the possibility of re-infection:
- try to wear comfortable and high-quality shoes (to prevent excessive sweating of the feet);
- It is recommended to change socks and tights every day;
- use only individual shoes. For those receiving treatment for onychomycosis, shoes should be treated at the beginning of treatment, at least once a month during the entire treatment period and after its completion;
- if necessary, use antiperspirants for the feet;
- use a personal nail care kit (scissors, files);
- use antifungal external agents (sprays, creams and pens) before and after visiting public places (swimming pool, bath, gym);
- identify the source of fungal infection in the family and treat it at the same time.
Periodic antifungal treatment of personal items, shoes, bathtubs, floors and rugs is recommended. For these purposes, you can use 40% acetic acid solution, 1% alcohol solution of chlorhexidine (prescribed by a doctor) and disinfectant solutions. Linen can be boiled in 1-2% soap-soda solution for 20-30 minutes, ironed at maximum temperature.























